|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Bloat (Torsion) |
||||||
|
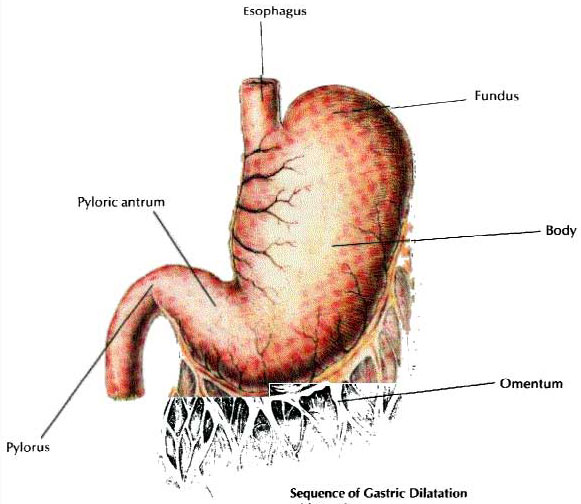
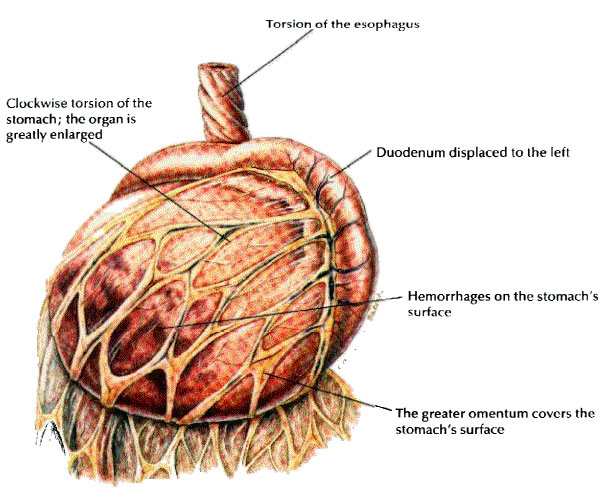
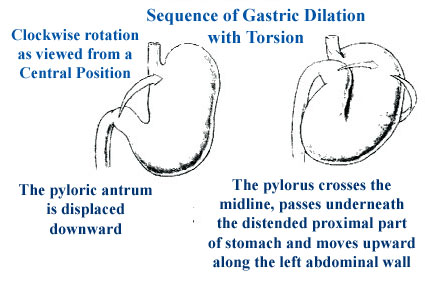
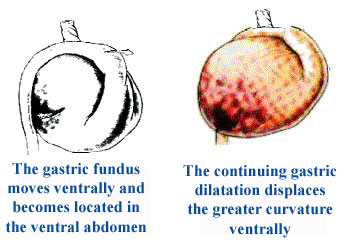
Gastric dilatation-volvulus (GDV) is an acute, life threatening disorder that is a medical and surgical emergency. Early recognition and treatment are essential for a successful outcome. Gastric dilatation refers to distension of the stomach, usually with swallowed air. Gastric dilatation may or may not be complicated by volvulus. GDV occurs when the stomach rotates on its long axis, resulting in complete gastric outflow obstruction. Concurrent obstruction of the gastro-esophageal junction (beginning of the stomach where it attaches to the esophagus) prevents relief of fluid and gas accumulation by vomiting or belching. Massive gastric distension impairs blood flow through the veins of the abdomen causing shock and toxicity. The intestines are affected causing the body to become acidic and predisposes the body to a coagulation disorder in which the body is unable to clot blood properly. The spleen is often affected and it swells causing more toxicity. The stomach wall also swells and due to loss of blood supply may also die. CAUSE: The cause of GDV/Torsion Bloat is unknown. An anatomic predisposition may play a role. Deep- Chested dogs like Shar-Pei are more commonly affected. Overeating, exercise immediately after or before eating may predispose to GDV. SIGNS: Acute onsets with abdominal distension, which will feel, like a drum. Non-productive retching and belching Salivating, restlessness, and respiratory distress are also observed. Radiography Metabolic acidosis is most common Low blood potassium will cause heart arrhythmias and muscle weakness Sedation to pass a tube into the stomach if possible. If passing of the tube is not possible-place several large bore needles into the distended stomach to relieve gas. If above not possible-surgery is needed immediately. Place an IV –administer fluids, potassium chloride, administer antibiotics and steroids to help avert shock. Monitor and treat cardiac arrhythmias The goals of surgical intervention are the following: Reposition the stomach and spleen Removing damaged stomach and splenetic tissue Permanently fixing the stomach to the abdominal wall to prevent future occurrences. It is beyond the scope of this article to describe the different procedures.
Site Researched and Produced by ©Kavishi Shar-Pei |
||||||